The many benefits of fully or strictly protected MPAs, also known as “Super MPAs”
Fully or strictly protected Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are a category of MPA offering the strictest level of protection, corresponding to the IUCN MPA category 1a (Strict Nature Reserve). They typically prohibit all industrial, extractive and destructive uses and activities that disturb marine life and habitats such as fishing, mining, mineral extraction, dredging, aquaculture and construction etc. They are called by different names, most commonly “No-Take Zones” or “integral marine reserves”.
Watch the video: Our friends’ quest for Emerald Bay
To mark the release of Oceana’s report looking at the threats European Marine Protected Areas face and the prevalence of marine “paper parks” in Europe, we’re releasing a short video animation. Join our friends, pregnant octopus, little seahorse, brainy fish and angel shark, on their quest for Emerald Bay Marine Protected Area and find out what they will see over the border…
Share the video:
Additionally, the video can be downloaded here by right-clicking in the new windows’s video player and selecting “Save video as…” option.
The following series of illustrations highlights the benefits of these no-take zones for marine biodiversity, fish and food provisioning, jobs and livelihoods of fishers, and how they are critical for climate change resilience. Please right-click on an image and select “Save image as…” if you wish to download it.
Oceana campaigns for their establishment as they are our best ally to halt marine biodiversity loss, the climate crisis and rebuild abundant oceans and fisheries.
* * *
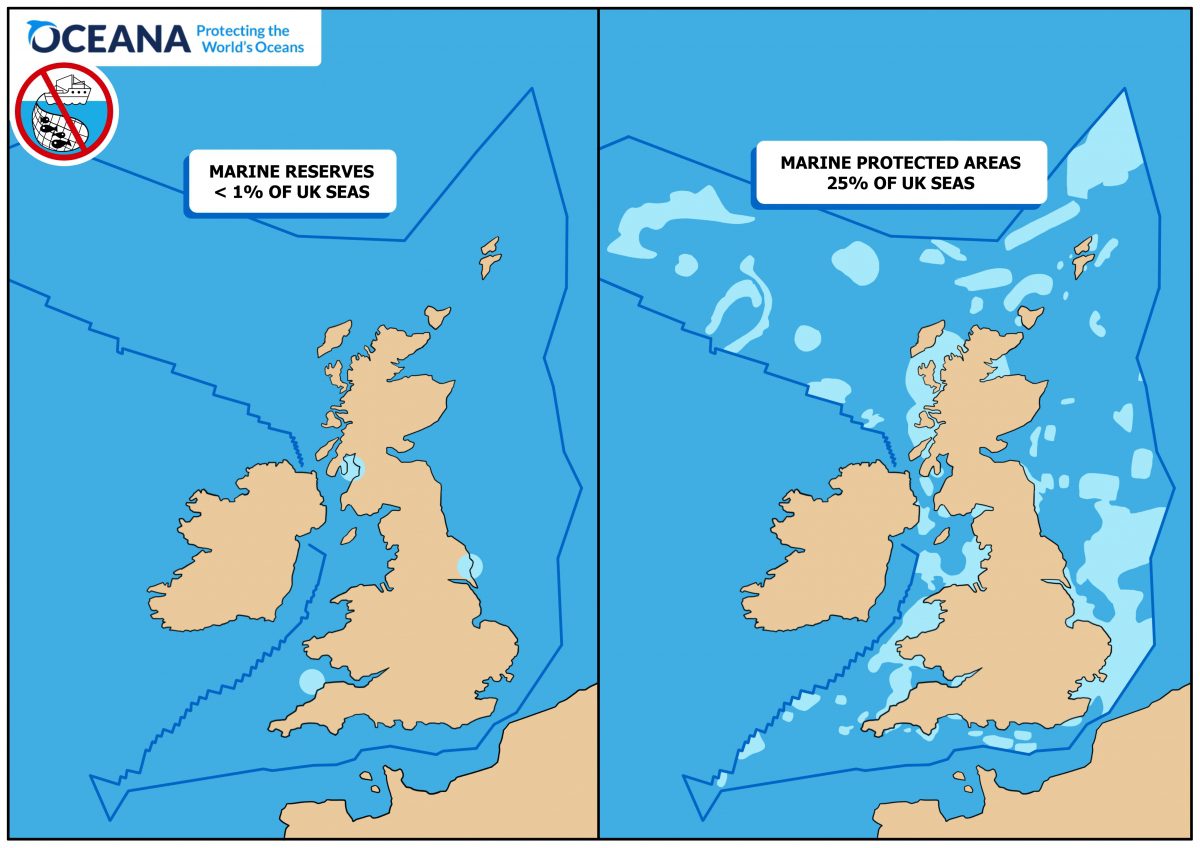
The UK Marine Protected Areas network covers about 30% of its seas, but no-take marine reserves cover less than 0.01% of these waters, whereas they are the most effective at rebuilding ocean resilience.
Share this:
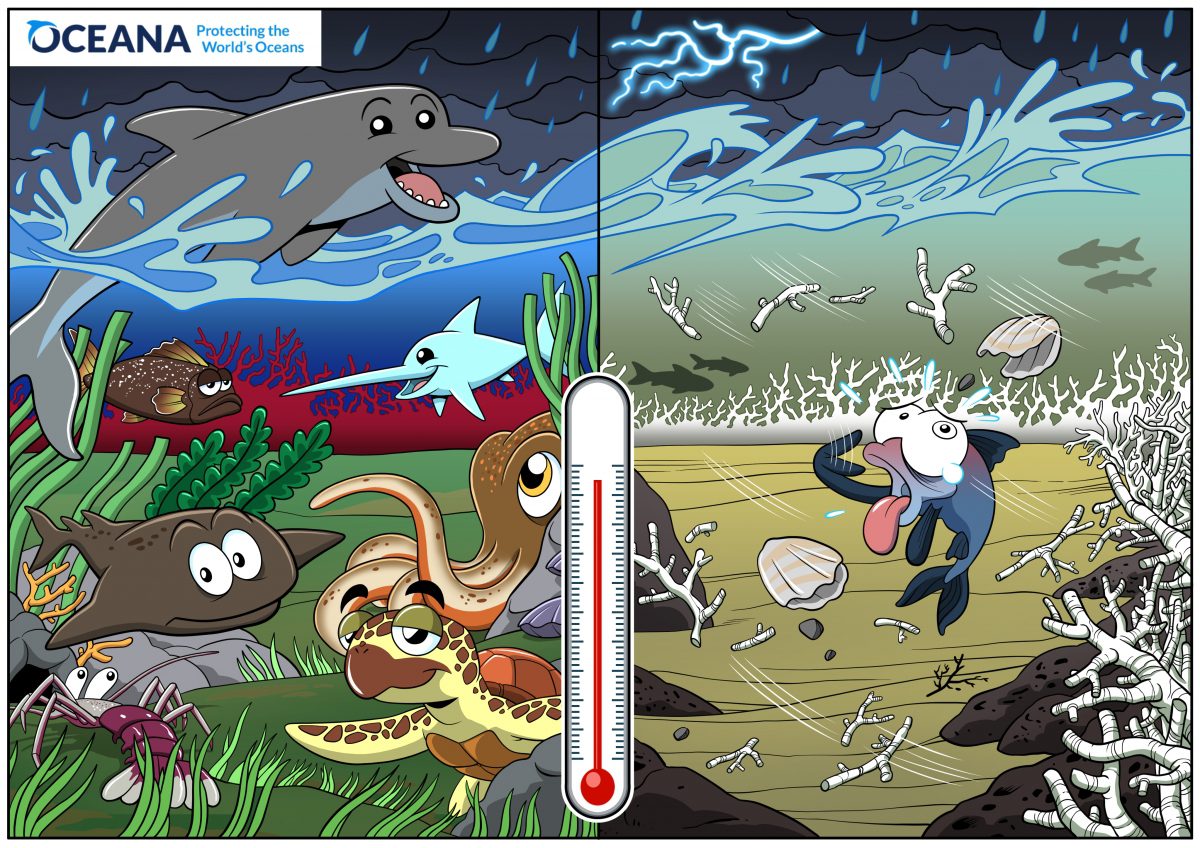
No-take zones significantly increase biodiversity by multiplying up to 6 times the abundance of fish, compared to unprotected waters. They increase fecundity and act as nurseries for eggs, larvae and juveniles.
Share this:
By creating more complex ecosystems, no-take zones are more resilient to climate change than less protected areas. They act as a refuge for species who can rest, feed, grow and reproduce safely. Healthy marine ecosystems respond better to stress factors than disturbed ones.
Share this:
In no-take zones, the use of the most destructive fishing gear, like bottom trawling, that destroys the seafloor and is highly unselective, is not allowed.
Share this: